What Causes Cellulite?

For over 40 years I've been asked by patients, "What causes cellulite, why am I predisposed to it - and most importantly - how can I get rid of it?" As a 60+ year old woman, I've spent years craving a cellulite secret myself. Here is what you need to know about reducing the appearance of cellulite.
What causes cellulite and are you predisposed to it?
As a dermatologist, I know that cellulite is caused by the way your skin's fat lobules are situated in the adipose layer of your skin. Your fat lobules are clustered between the fibrous cords that support the fat (adipose) layer of your skin. You are predisposed to cellulite if your fibrous cords allow the fat lobules to bulge upwards from the adipose layer of your skin into the dermal layer above.
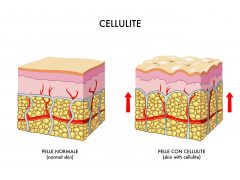
The cause of cellulite lies in the adipose layer of your skin.
The adipose layer of your skin is made up of:
- groups of fat lobules (seen here as yellow spheres); and
- fibrous cords (seen as white parallel vertical lines) that run between the groups of fat lobules. These fibrous cords hold down the fat lobules and connect them to the underlying muscle and the dermis that sits above the adipose layer (represented by the light pink layer in this diagram).
Everyone has this same structure of fat lobules interspersed between fibrous cords in their adipose layer. But some people's fibrous cords allow their’ fat lobules to protrude upwards more than other people's, and this is what causes cellulite.
Can you cure cellulite? No, but you can make your skin look better so the cellulite is less noticeable.
What do I - a 60+ year old dermatologist and woman who is prone to cellulite - do to make my cellulite look less noticeable?
- I exercise. This really helps me.
- I watch my diet to keep the fat lobules as reigned-in as I can manage.
- I keep the cellulite-prone skin soft, smooth, satiny, glowing and youthful to soften the appearance of dimpling.
 I use my Ultra-Fast Body Smoothing Triple Action Kit to help my skin stay glowing and satiny smooth. It works for adults of all ages and it is never too late to reclaim glowing and soft skin - really.
I use my Ultra-Fast Body Smoothing Triple Action Kit to help my skin stay glowing and satiny smooth. It works for adults of all ages and it is never too late to reclaim glowing and soft skin - really.
What causes cellulite to increase or go away?
Since cellulite is caused by the bulging of fat lobules between fibrous cords in the adipose layer of your skin,
- the dimpling of cellulite will show more when more fat accumulates in the fat lobules,
- the dimpling will show less when the amount of fat held in the lobules is reduced.
If you are predisposed to cellulite, nothing you can do will change the appearance of it except altering the amount of fat held in the lobules.
Argh! It's a sad truth, and it is important to understand. The cause of cellulite is the structural relationship between fat lobules and fibrous cords in the adipose layer and some people have fibrous cords that allow the fat to bulge upward causing a dimpling appearance to the overlying skin.
Where are you most likely to be predisposed to cellulite?
The areas most prone to cellulite are the buttock, hips and thighs.
What causes you to be predisposed to cellulite?
- Women are more prone to cellulite than men or children. As many as 80-90% of women develop cellulite to some extent after puberty.
- Women are prone to have lax fibrous cords between the fat lobules in their adipose layer. A woman does not need to be overweight to have cellulite. They simply need to have lax fibrous cords that allow the lobules of fat to bulge upward. So, yes, even slim women can have cellulite!
- Cellulite can be genetic. If women in your family have cellulite then you may be more prone to it.
- Wearing tight underwear has been associated with an increased incidence of cellulite. This is hypothesized to be secondary to reduced circulation in the skin below.
- Women who are overweight have more fat in their fat lobules and will be more prone to cellulite.
- A sedentary lifestyle will increase your risk of cellulite.
When do women start getting cellulite?

- The dimpling of cellulite typically starts after puberty.
- Pregnancy can worsen cellulite.
- Cellulite will also get worse as a woman ages.
Oh fun!
Now that you know the cause of cellulite, what can you do to get rid of it?
Do creams and cellulite treatments that you see advertised work to cure cellulite? Sadly, no, or not entirely. There are many creams and treatments touted to treat cellulite. Most don't have any good scientific proof.
The American Academy of Dermatology lists a number of approved treatments for cellulite. This is a good page to keep up with technologic advances in cellulite treatment. Options at present include
- lasers,
- subcision (cutting the fibrous cords - ouch!),
- filler injection etc.
- Liposuction, and
- cryolipolysis (such as Coolsculpt) may help some women.
Unfortunately, none of these cellulite treatments are universally considered successful for long term improvement of cellulite, though individual results may vary.
 My opinion is that the best way to reduce the appearance of cellulite is with exercise and weight loss - which is also good for your overall health. If and when a good treatment becomes available, we can add this to our healthy lifestyle and really rock the look of dimple-free health and vitality. If you are predisposed to cellulite, take comfort in the fact that you are not alone. Know that it will get worse with weight gain, and as you age. I think almost every woman knows this - I know I do.
My opinion is that the best way to reduce the appearance of cellulite is with exercise and weight loss - which is also good for your overall health. If and when a good treatment becomes available, we can add this to our healthy lifestyle and really rock the look of dimple-free health and vitality. If you are predisposed to cellulite, take comfort in the fact that you are not alone. Know that it will get worse with weight gain, and as you age. I think almost every woman knows this - I know I do.
References
Neil Sadick, MD, Treatment for cellulite, Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019 Feb; 5(1): 68–72.Published online 2018 Oct 22. doi: 10.1016/j.ijwd.2018.09.002
Roberto Amore, Treatment of Dimpling from Cellulite, Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2018 May; 6(5): e1771. Published online 2018 May 18.










